In the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, Initial Access Brokers (IABs) play an increasingly crucial role in enabling ransomware operations. One name recently catching the attention of cybersecurity experts is ToyMaker, a financially motivated IAB that has been linked to facilitating double extortion ransomware attacks, notably assisting the CACTUS ransomware group. Using a custom malware named LAGTOY (also known as HOLERUN), ToyMaker is reshaping how ransomware gangs gain a foothold in high-value organizations.
This comprehensive analysis will explore ToyMaker’s tactics, the functionality of LAGTOY, the ransomware ecosystem it fuels, and proactive measures organizations must adopt to defend against such evolving threats.
Who is ToyMaker?
ToyMaker is assessed with medium confidence to be a financially motivated threat actor, active in the cybercrime ecosystem primarily as an Initial Access Broker. IABs specialize in infiltrating systems, performing reconnaissance, and then selling access to ransomware gangs and other malicious actors. This specialization allows ransomware groups to bypass the risky and time-consuming process of breaching organizations themselves.
ToyMaker’s signature move involves scanning for vulnerable systems across internet-facing applications, deploying LAGTOY to compromised systems, and later selling access to ransomware operators like CACTUS.
The involvement of ToyMaker demonstrates the increasing professionalization and specialization within the cybercrime underworld, where supply chain-like structures allow threat actors to focus on their strengths.
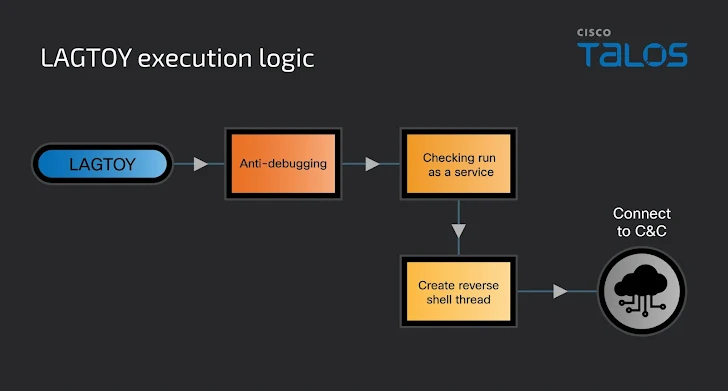
Understanding LAGTOY Malware
LAGTOY, also tracked as HOLERUN, is ToyMaker’s custom-developed malware, designed to create reverse shells and execute arbitrary commands on infected endpoints.
Key Features of LAGTOY:
- Command and Control Communication: LAGTOY communicates with a hardcoded C2 (command-and-control) server to fetch and execute commands.
- Privilege Execution: It can execute processes and commands under specified user privileges, aiding lateral movement.
- Memory Dumping: Attackers use Magnet RAM Capture post-compromise to create memory dumps for credential harvesting.
- Persistence Mechanisms: The malware ensures longevity by exploiting SSH connections and deploying remote access tools like AnyDesk and eHorus Agent.
- Sleep Mechanism: Commands are executed at controlled intervals (11,000 milliseconds) to evade detection.
This stealth and functionality make LAGTOY a powerful tool for establishing and maintaining access until it is sold to ransomware operators.
Attack Lifecycle: From Breach to Ransom
The cyberattack lifecycle involving ToyMaker and CACTUS ransomware can be broken down into several phases:
1. Vulnerability Scanning
ToyMaker scans the internet for known vulnerabilities in widely-used applications, such as outdated VPNs, exposed RDP ports, and web applications.
2. Initial Access
Upon identifying a vulnerable system, ToyMaker deploys LAGTOY to establish a foothold, creating remote access channels and capturing vital system information.
3. Credential Harvesting
Using tools like Magnet RAM Capture, ToyMaker collects memory dumps to harvest usernames, passwords, and session tokens.
4. Access Sale
Rather than engaging directly in ransomware attacks, ToyMaker sells this access to groups like CACTUS, which specialize in double extortion attacks.
5. Ransomware Deployment
CACTUS ransomware affiliates use the provided credentials to exfiltrate sensitive data and encrypt systems, later demanding ransom payments while threatening to release stolen data.
6. Long-Term Access Setup
Persistence mechanisms like SSH backdoors and remote desktop tools are installed to maintain access even if the initial breach is discovered.
What is CACTUS Ransomware?
CACTUS is a double extortion ransomware operation that encrypts victim data and simultaneously steals sensitive files, threatening to leak it if the ransom isn’t paid.
Key Characteristics of CACTUS Ransomware:
- Encrypted Communications: CACTUS uses robust encryption for its communications, complicating forensic investigations.
- Sophisticated Encryption: Ransomware payloads are encrypted even before deployment.
- Focus on Enterprises: The group targets large organizations, often demanding millions in ransom.
The group has gained notoriety for aggressive tactics, short dwell times, and careful targeting to maximize the chance of payment.
Why ToyMaker Prefers Selling Access Instead of Deploying Ransomware
While ransomware groups often handle the end-to-end operation themselves, ToyMaker operates differently. Instead of conducting the data exfiltration and encryption, ToyMaker focuses on access acquisition and sale.
Advantages for ToyMaker:
- Lower Operational Risk: Selling access reduces exposure to law enforcement crackdowns.
- Faster Monetization: Immediate profit without waiting for ransom negotiations.
- Broader Market: Can sell access to multiple groups, including ransomware, espionage actors, and cyber mercenaries.
This division of labor mirrors legitimate business practices, with IABs acting as wholesalers and ransomware groups as retailers.
How ToyMaker and CACTUS Attack Organizations
Anatomy of a ToyMaker-facilitated CACTUS ransomware attack typically involves:
- Exploitation of VPN vulnerabilities
- Deployment of LAGTOY malware
- Execution of Magnet RAM Capture to steal credentials
- Establishing SSH tunnels for persistence
- Selling credentials to CACTUS ransomware group
- CACTUS affiliates performing network reconnaissance
- Data exfiltration and system encryption
- Double extortion: ransom demand and data leak threat
Defending Against ToyMaker and CACTUS
Organizations must adopt a layered defense strategy to guard against ToyMaker and CACTUS ransomware attacks.
1. Patch Management
- Prioritize Critical Vulnerabilities: Especially VPNs, RDP, and internet-facing applications.
- Automated Patch Deployment: Use patch management tools for faster updates.
2. Network Segmentation
- Zero Trust Architecture: Assume breach and enforce least privilege access.
- Internal Firewalls: Segment sensitive data and production environments.
3. Endpoint Protection
- Behavioral Analysis: Use EDR solutions that detect anomalous behavior, not just known malware signatures.
- Memory Protection: Tools that detect attempts to dump memory.
4. User Authentication
- MFA Everywhere: Deploy Multi-Factor Authentication for all accounts, especially administrative ones.
- Credential Hygiene: Regularly rotate and monitor credentials.
5. Backup and Recovery
- Offline Backups: Maintain copies disconnected from the network.
- Regular Testing: Ensure that backup restoration procedures are effective.
6. Threat Intelligence and Monitoring
- Honeypots and Deception Technology: Deploy traps to detect intrusions early.
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of network and endpoint activity.
Conclusion
The rise of ToyMaker as an Initial Access Broker selling system access to ransomware operators like CACTUS highlights how cybercriminal activities have evolved into a highly specialized industry. By leveraging custom tools like LAGTOY, ToyMaker efficiently infiltrates organizations, setting the stage for devastating ransomware attacks.
Organizations must remain vigilant, proactively strengthen their cybersecurity posture, and adopt a multi-layered defense strategy. As cyber threats continue to advance in sophistication, collaboration between cybersecurity vendors, threat intelligence firms, and enterprise security teams becomes more critical than ever.
The case of ToyMaker and CACTUS underscores a simple but harsh reality: in today’s digital world, no organization is too small or too secure to be targeted. Staying informed and prepared is not just a best practice — it’s a necessity.














Add comment